The latest issue of international academic journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America published the paper by JSNU Professor Shi Yanhui and Professor Cao Changsheng on their teams’ discovery of two compounds that able to kill cancer cells.

The paper, titled “Self-assembled ruthenium (II) metallacycles and metallacages with imidazole-based ligands and their in vitro anticancer activity,” was published in the March 5 issues of PNAS.
It was co-authored by Associate Professor Zhang Peng from School of Life Science, JSNU and contributed by Professor Peter J. Stang from University of Utah.
“Cancer is one of the most deadly diseases. In the treatment of cancer, the success of platinum compounds has propelled the application of transition metal complexes for therapeutic design. Ruthenium compounds have emerged as promising anticancer candidates. Self-assembly strategy allows the construction of large-sized and high-molecular-weight supermolecules that may display antitumor efficacy and selectivity due to their unique biochemical properties. Herein, we describe the construction of Ru(II) tetranuclear rectangular macrocycles and hexanuclear trigonal prisms by self-assembly. The self-assembled compounds containing the 5,8-dioxido-1,4-naphtoquinonato scaffold exhibited enhanced anticancer activity on colon, breast, cervical, lung, and liver cancer cells, and decreased cytotoxicities in HEB and THLE-2 normal cells. Two of these compounds are able to kill cancer cells more effectively and selectively than cisplatin.”
Abstract:
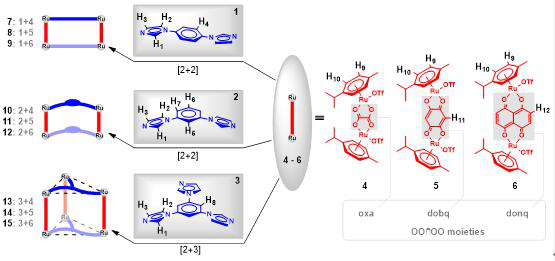
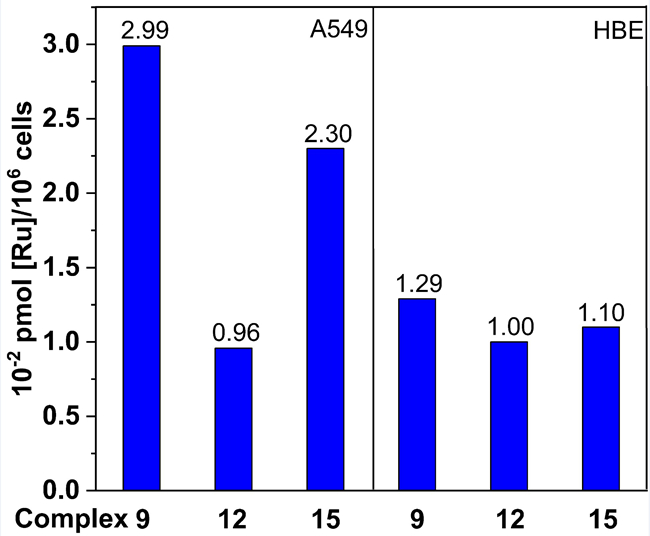
Six tetranuclear rectangular metallacycles were synthesized via the [2+2] coordination-driven self-assembly of imidazole-based ditopic donor 1,4-bis(imidazole-1-yl)benzene and 1,3-bis(imidazol-1-yl)benzene, with dinuclear half-sandwich p-cymene ruthenium(II) acceptors [Ru2(µ-η4-oxalato)(η6-p-cymene)2](SO3CF3)2, [Ru2(µ-η4-2,5-dioxido-1,4-benzoquinonato)(η6-p-cymene)2](SO3CF3)2 and [Ru2(µ-η4-5,8-dioxido-1,4-naphtoquinonato)(η6-p-cymene)2](SO3CF3)2, respectively. Likewise, three hexanuclear trigonal prismatic metallacages were prepared via the [2+3] self-assembly of tritopic donor of 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene with these ruthenium(II) acceptors respectively. Self-selection of the single symmetrical and stable metallacycle and cage was observed although there is the possibility of forming different conformational isomeric products due to different binding modes of these imidazole-based donors. The self-assembled macrocycles and cage containing the 5,8-dioxido-1,4-naphtoquinonato (donq) spacer exhibited good anticancer activity on all tested cancer cell lines (HCT-116, MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, HeLa, A549, and HepG-2), and showed decreased cytotoxicities in HBE and THLE-2 normal cells. The effect of Ru and imidazole moiety of these assemblies on the anticancer activity was discussed. The study of binding ability of these donq-based Ru assemblies with ctDNA indicated that the complex 9 with 180° linear 1 ligand has the highest bonding constant Kb to ctDNA.
